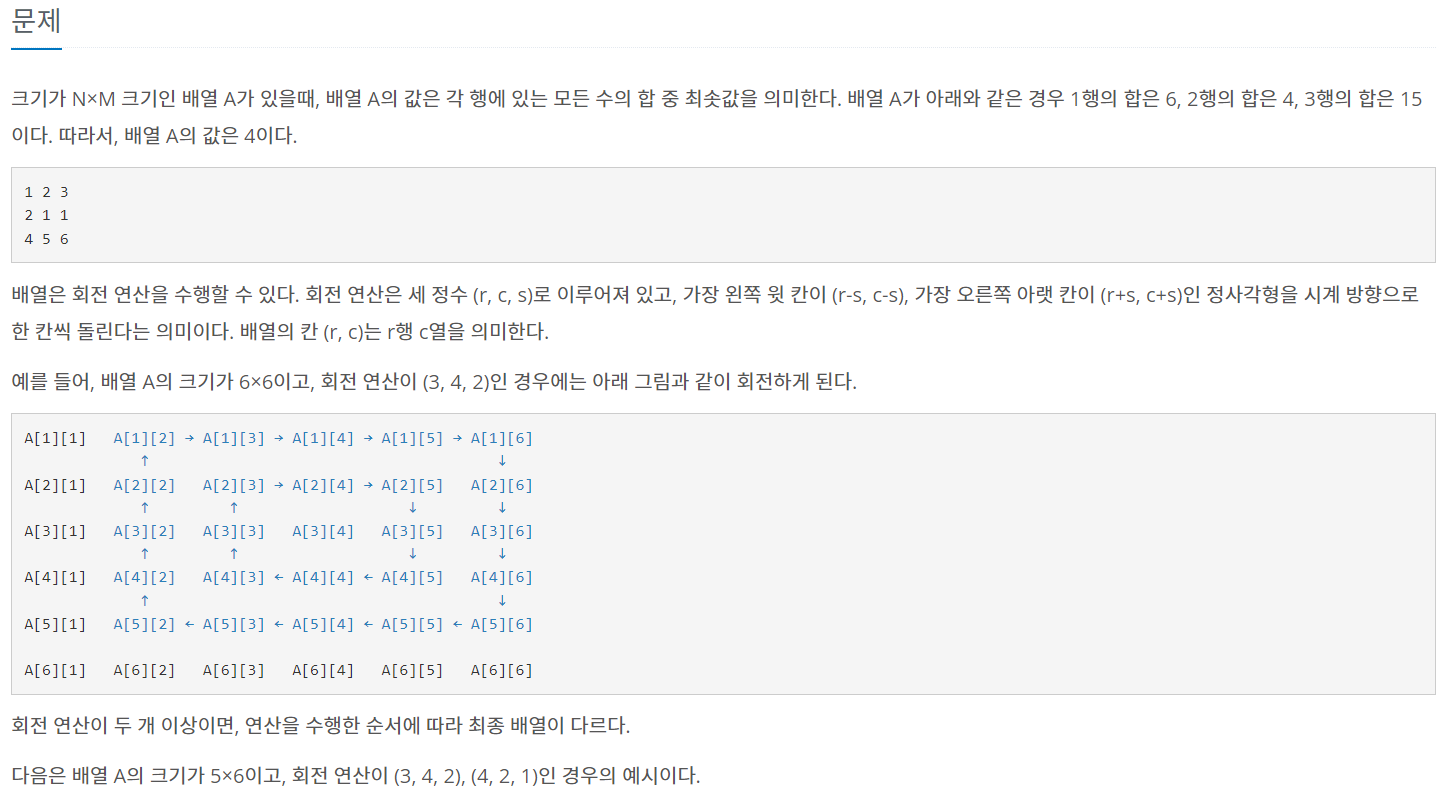
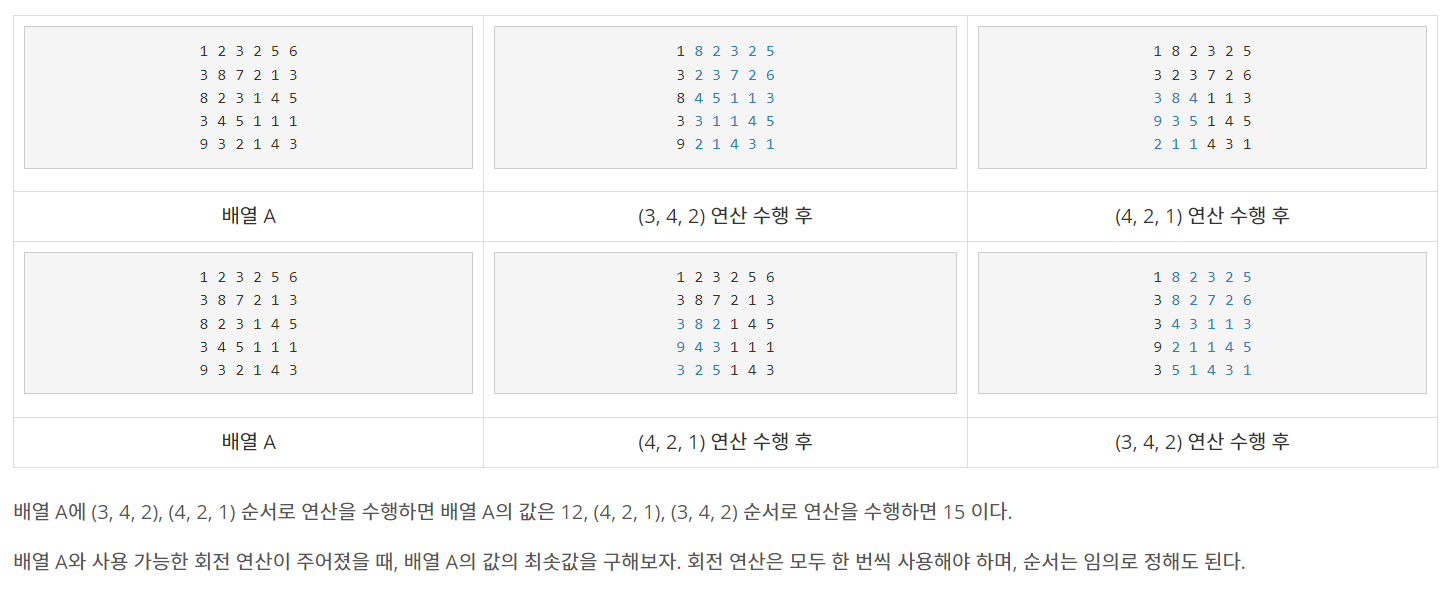
순열을 통해서 회전순서의 가능한 모든 경우를 구하고
각 경우 별로 배열을 돌려서 최소값을 찾는 문제이다.
조건이 많고 배열을 돌릴 때 이동하는 개념을 잘 이해하지 못 해서 푸는데 굉장히 오래 걸렸다.
중심좌표를 기준으로 배열을 그려보며 풀면 이해가 된다.
코드에 주석을 달아놓았다.
package hw;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main_17406_배열돌리기4 {
/*
* 회전순서 순열을 구한다
* 구해진 순열마다 배열을 돌려보면서 모든 경우에서 최소값을 구한다
* 이때 배열은 깊은 복사를 통해서 원본 배열은 그대로 두고
* 계속 해서 임시 배열을 복사해서 사용해야 하며
* 배열을 돌리는 오른쪽, 왼쪽, 위, 아래 각각의 범위를
* 잘 생각해주어야 했던 문제
*/
static int N, M, K; //배열의 가로, 세로, 회전횟수
static int [][] arr; //원본 배열
static int [][] rotate; //회전정보를 넣어줄 배열
static int [][] perm; //순열에서 사용할 배열
static boolean [] visited; //순열에서 방문처리 해줄 배열
static int res; //최종 결과값
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//회전정보와 배열의 좌표를 맞춰주기 위해서
//배열 크기에 +1을 해준다
arr = new int [N+1][M+1];
//회전기준 x좌표, y좌표, 회전 횟수를 입력받기 위한 회전 정보 배열
rotate = new int [K][3];
//순열을 돌려서 만들어진 순서를 넣어줄 배열
perm = new int [K][3];
//순열 생성 시 방문 확인 해 줄 배열
visited = new boolean[K];
res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//주어진 배열 정보를 입력 받는다
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=1; j<M+1; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
//회원 정보 저장
for(int i=0; i<K; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=0; j<3; j++) {
rotate[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
Permutation(0);
System.out.println(res);
}
//순열을 생성하는 메소드
//순열을 생성해서 기저조건에 도달할 때마다
//회전 메소드를 돌려줄 것임
public static void Permutation(int depth) {
//기저 조건
if(depth == K) {
//새로운 배열을 순열이 완성될 때마다 만들어주자
int [][] tempArr = new int [N+1][M+1];
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<M+1; j++) {
tempArr[i][j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
//복사된 배열과 완성된 순열을 가지고 회전을 돌린다
for(int i=0; i<K; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=perm[i][2]; j++) {
int x = perm[i][0];
int y = perm[i][1];
tempArr = rotation(tempArr, x, y, j);
}
}
//다 돌리고 나면 다시 한번 배열을 돌면서
//행의 최소값을 구한다
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for(int j=1; j<M+1; j++) {
sum += tempArr[i][j];
}
res = Math.min(res, sum);
}
return;
}
//rotate 배열의 정보를 하나씩 뽑아서
//perm 배열에 넣어주자
for(int i=0; i<K; i++) {
if(visited[i]) {
continue;
}
else {
perm[depth] = rotate[i];
visited[i] = true;
Permutation(depth+1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static int [][] rotation(int [][] tempArr, int x, int y, int c){
//가장 처음 배열칸을 미리 빼놓고 다른 변수에 저장해놓자
int temp = tempArr[x-c][y-c];
//위로 올리기
for(int i=x-c+1; i<=x+c; i++) {
tempArr[i-1][y-c] = tempArr[i][y-c];
}
//왼쪽으로 밀기
for(int i=y-c+1; i<=y+c; i++) {
tempArr[x+c][i-1] = tempArr[x+c][i];
}
//아래로 밀기
for(int i=x+c-1; i>=x-c; i--) {
tempArr[i+1][y+c] = tempArr[i][y+c];
}
//오른쪽으로 밀기
for(int i=y+c-1; i>=y-c; i--) {
tempArr[x-c][i+1] = tempArr[x-c][i];
}
//다 밀었으면 마지막 남은 칸에 temp 변수에 저장해놓은 값을 넣어주자
tempArr[x-c][y-c+1] = temp;
return tempArr;
}
}
'알고리즘 > BeakJoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2644 촌수계산 Java (0) | 2023.01.12 |
|---|---|
| 백준 1260 DFS와 BFS Java (0) | 2023.01.11 |
| 백준 2667 단지번호붙이기 Java (0) | 2023.01.05 |
| 백준 2630 색종이 만들기 Java (0) | 2023.01.05 |
| 백준 2563 색종이 Java (0) | 2022.12.25 |
