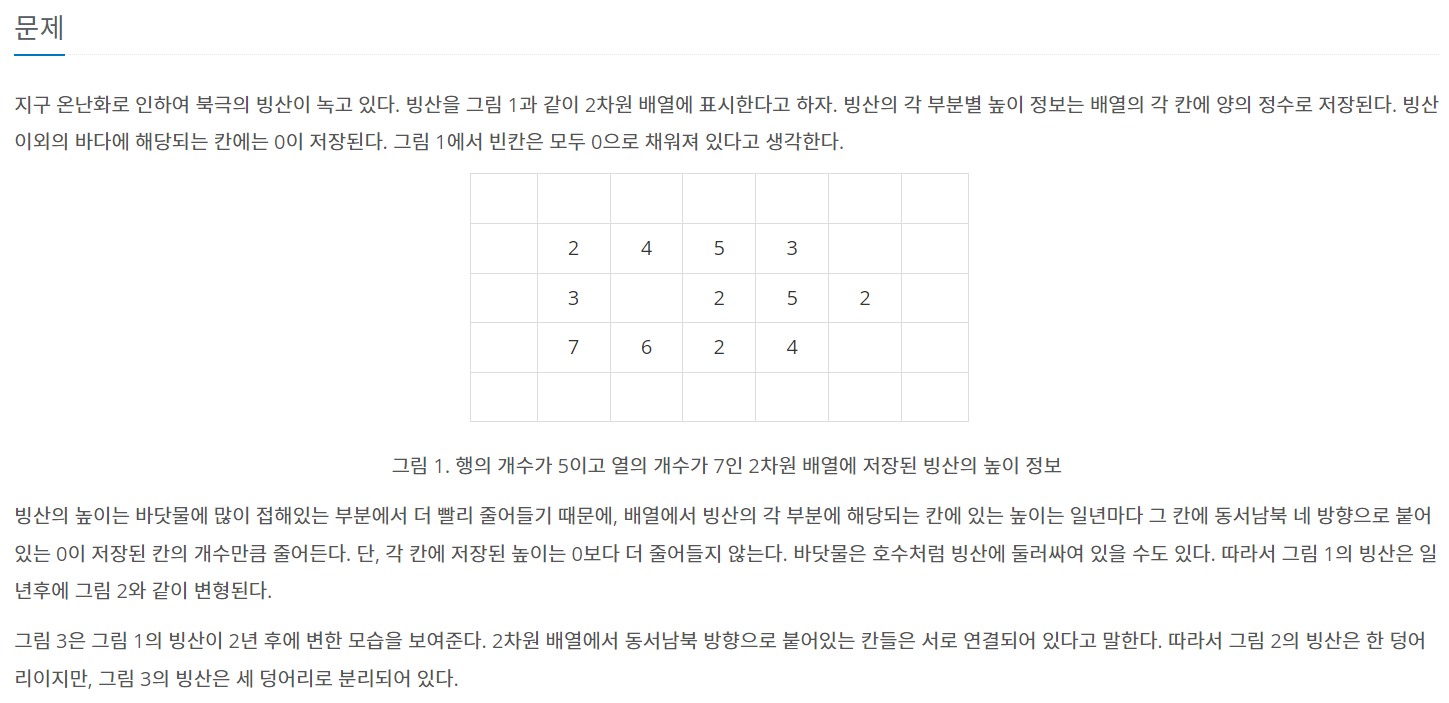
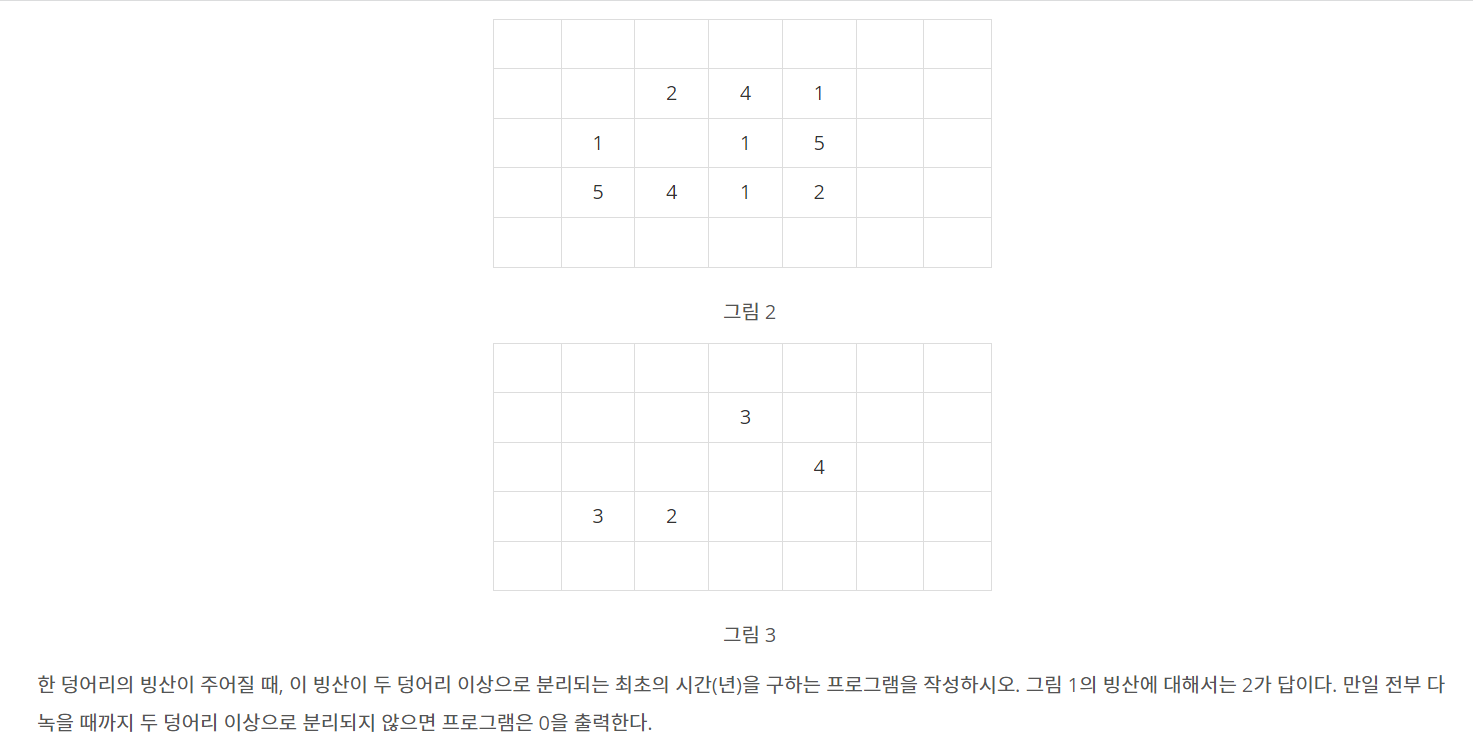
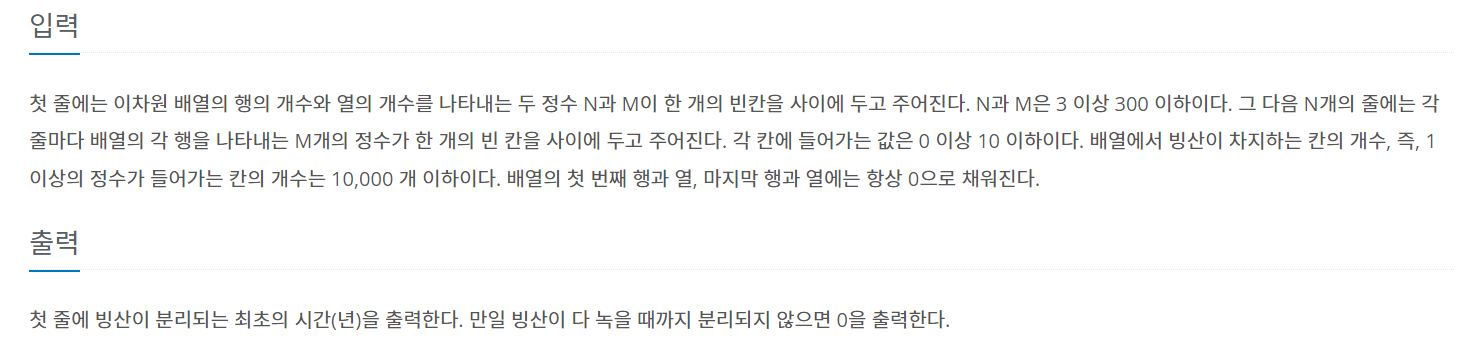
bfs를 돌면서 빙산의 4방에 바다가 몇개 있는지를 list에 담아놓고 한번에 녹여주었다.
반복을 돌 때마다 배열이나 리스트를 초기화 시켜주어야 하기 때문에 생각을 많이 해야하는 문제였다.
코드에 주석을 자세하게 달아놓았다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
/*
4방탐색 후 0의 개수만큼
얼음이 녹음
두 덩어리 이상으로 분리되는 최초의 시간을 구하기
두 덩어리 이상 분리 안 되면 0 출력
DFS로 풀어보자
DFS + BFS로 풀어야 할 듯????
*/
static int N, M; //행, 열
static int [][] arr; //배열
static boolean [][] visited; //방문 확인
//4방 탐색
static int [] dx = {1, 0, -1, 0};
static int [] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
static List<int[]> list;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
//전역변수 초기화
arr = new int [N][M];
//배열에 값 채워넣기
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int year = 0;
while (true) {
int landCnt = 0;
//bfs를 돌고 나와서는 방문 처리 배열을
//초기화 해줘야 함
//bfs 한번 돌고 나오면 arr 값이 바뀜
visited = new boolean[N][M];
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0 && visited[i][j] ==false) {
bfs(i, j);
landCnt++;
}
}
}
//list의 값대로 arr의 값에서 빼기
for(int k=0; k<list.size(); k++){
int x = list.get(k)[0];
int y = list.get(k)[1];
int cnt = list.get(k)[2];
arr[x][y] -= cnt;
if(arr[x][y]<0){
arr[x][y] = 0;
}
}
if(landCnt > 1){
System.out.println(year);
break;
}
if(landCnt == 0){
System.out.println(0);
break;
}
year++;
}
//0이 아닌 숫자마다
//4방에 0이 몇개 있는지 세어보고
//그거를 어딘가에 저장해놔야 할 듯?
}
//이어진 빙산을 따라가보자
public static void bfs(int x, int y){
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(x);
q.offer(y);
visited[x][y] = true;
countSea(x, y, 0);
while (!q.isEmpty()){
int curX = q.poll();
int curY = q.poll();
for(int idx=0; idx<4; idx++){
int nnx = curX + dx[idx];
int nny = curY + dy[idx];
if(nnx >= 0 && nnx < N && nny >= 0 && nny < M){
if(arr[nnx][nny] != 0 && !visited[nnx][nny]){
countSea(nnx, nny, 0);
visited[nnx][nny] = true;
q.offer(nnx);
q.offer(nny);
}
}
}
}
}
//하나의 빙산을 기준으로 주변 바다를 세는 메소드
//하나의 바다가 중복해서 빙산에게 영향을 줄 수 있음
//방문처리는 필요 없을 듯?
public static void countSea(int x, int y, int cnt){
for(int idx = 0; idx<4; idx++){
int nx = x + dx[idx];
int ny = y + dy[idx];
//범위 안에 있고
//값이 0 이라면
if(nx>=0 && nx < N && ny >= 0 && ny < M){
if(arr[nx][ny] == 0){
cnt++;
}
}
}
list.add(new int[] {x, y, cnt});
}
}'알고리즘 > BeakJoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2583 영역 구하기 Java (0) | 2023.01.30 |
|---|---|
| 백준 10026 적록색약 Java (0) | 2023.01.27 |
| 백준 2636 치즈 Java (0) | 2023.01.26 |
| 백준 5014 스타트링크 Java (0) | 2023.01.20 |
| 백준 2468 안전 영역 Java (0) | 2023.01.19 |
